




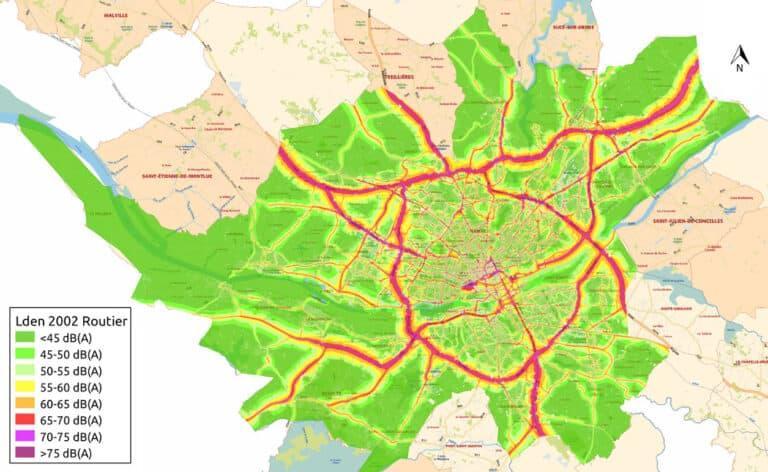
Noise mapping is a vital tool in assessing and managing environmental noise pollution. This article provides an in-depth exploration of noise mapping, including its definition, types, procedures, software applications, and benefits. It specifically focuses on traffic noise monitoring, as traffic is a significant source of environmental noise in urban areas. By understanding the intricacies of noise mapping, we can develop effective strategies to mitigate noise pollution, improve public health, and enhance the quality of urban living.
Introduction: Noise pollution is a growing concern in urban areas, affecting the well-being of residents and the overall livability of cities. Noise mapping is a comprehensive approach that utilizes advanced technologies, data analysis, and visualization techniques to assess and manage environmental noise. By mapping noise levels across different urban regions, decision-makers can make informed choices to address noise pollution and improve the quality of life for citizens.
Types of Noise Mapping: Noise mapping encompasses various types of maps that serve different purposes. Strategic noise maps provide a broad overview of noise levels across an entire city or region, while noise action plans focus on identifying noise sources and proposing mitigation measures. Noise monitoring maps offer real-time data, and noise exposure maps assess the cumulative impact of noise on human health and well-being.
Noise Mapping Procedure: The noise mapping process involves several key steps, including data collection, noise prediction modeling, integration with Geographic Information Systems (GIS), simulation, and visualization. The article will provide a comprehensive guide to the noise mapping procedure and highlight the importance of accurate data and model selection for reliable results.
Noise Mapping Software: Numerous software applications are available for noise mapping, each offering distinct features and capabilities. From user-friendly tools for beginners to advanced platforms for experts, this section will explore popular noise mapping software and their functionalities.
Noise mapping software plays a pivotal role in the noise mapping process by providing tools and functionalities for data analysis, modeling, visualization, and reporting. These software applications assist environmental experts, urban planners, and policymakers in comprehensively assessing noise pollution levels and formulating effective strategies for noise mitigation. Here, we explore some examples of popular noise mapping software:
Example 1: CadnaA (Computer-Aided Noise Abatement) CadnaA is a widely used software developed by DataKustik GmbH, designed specifically for noise mapping and environmental noise analysis. It offers a user-friendly interface and powerful features, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced noise professionals. CadnaA integrates noise measurement data, topographical information, and GIS data to create detailed noise maps for various applications.
Features:
Example 2: SoundPLAN SoundPLAN is another widely used noise mapping software developed by SoundPLAN GmbH. It caters to a broad range of noise mapping applications, from small-scale projects to large-scale city-wide mapping.
Features:
Example 3: IMMI (Integrated Noise Model) IMMI, developed by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States, is specifically designed for assessing aircraft noise and its impact on communities surrounding airports.
Features:
These examples showcase the diverse capabilities of noise mapping software and how they cater to different noise mapping requirements, from city-wide noise mapping to specialized applications like airport noise assessment. As technology advances, noise mapping software continues to evolve, integrating real-time data, IoT, and artificial intelligence to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and the overall effectiveness of noise management strategies.
Benefits of Noise Mapping: Noise mapping provides a wealth of benefits, including identifying high-exposure areas, evaluating noise mitigation measures, supporting urban planning decisions, and engaging with the public and stakeholders. The article will discuss these advantages and emphasize the importance of noise mapping in sustainable urban development.
Traffic Noise Monitoring: Traffic noise is one of the most common sources of environmental noise in urban areas. This section will delve into the characteristics of traffic noise, factors influencing its intensity, and methods of measuring and modeling traffic noise levels. Case studies will showcase successful traffic noise monitoring initiatives.
Noise Mapping and Health Impacts: Noise pollution has profound effects on public health, leading to stress, sleep disturbances, and various health issues. This section will explore the relationship between environmental noise and health outcomes, and how noise mapping can aid in public health protection.
Noise Mapping and Environmental Impact Assessment: Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) includes an evaluation of noise impacts during the planning and development of projects. This section will examine the role of noise mapping in EIA processes and showcase case studies highlighting its significance.
Noise Mapping for Noise Control and Abatement: Noise mapping serves as a valuable tool for identifying noise sources and devising effective abatement strategies. This section will discuss noise source identification, noise barrier design, and traffic management solutions.
Challenges and Limitations of Noise Mapping: Despite its usefulness, noise mapping comes with its challenges, such as data availability and quality, uncertainties in modeling, and public acceptance. The article will shed light on these limitations and suggest ways to address them effectively.
Case Studies of Successful Noise Mapping Projects: This section will present notable examples of successful noise mapping projects from different regions and industries. It will showcase how noise mapping has been instrumental in shaping noise management strategies and improving urban environments.
Future Perspectives and Advancements in Noise Mapping: Advancements in technology, such as real-time noise mapping and integration with the Internet of Things (IoT), hold great promise for the future of noise mapping. Machine learning applications can further enhance the accuracy and efficiency of noise prediction models.
Conclusion: Noise mapping is a powerful tool that plays a crucial role in shaping sustainable urban development and improving the quality of life for urban residents. By understanding the various aspects of noise mapping, from data collection to visualization and public engagement, stakeholders can collaboratively work towards reducing noise pollution and creating healthier, quieter, and more livable cities. Through continued research, innovation, and community involvement, noise mapping will continue to evolve as a valuable tool in environmental noise management and public health protection.




