CARBON CREDIT SCHEME
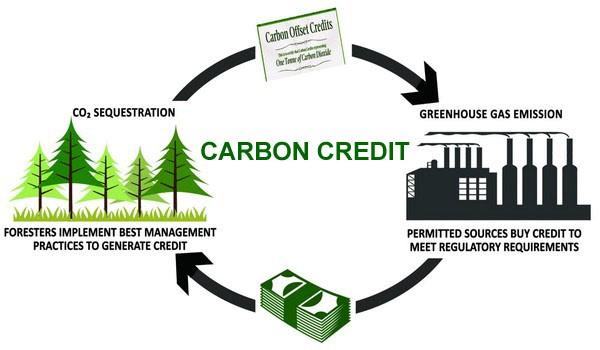
CARBON CREDIT SCHEME Share on whatsapp WhatsApp Share on facebook Facebook Share on twitter Twitter Share on linkedin LinkedIn Share on email Email Also Read Global CCS Report A carbon credit scheme, also known as a carbon offset scheme or carbon trading scheme, is a market-based approach designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. It operates […]
CARBON CREDIT SCHEME Read More »